Smart money trading guide [PDF] introduces you to the principles behind institutional trading, often called “smart money trading.” Instead of treating price movements as random, this guide shows how banks and hedge funds use price delivery algorithms, liquidity grabs, and order flow to influence price direction in the forex market.
Introduction
Trading successfully requires more than indicators and guesswork—it requires understanding how institutional players truly move the markets. This Smart money trading guide PDF introduces you to the principles behind institutional trading, often called “smart money trading.” Instead of treating price movements as random, this guide shows how banks and hedge funds use price delivery algorithms, liquidity grabs, and order flow to influence price direction in the forex market.
Inside, you’ll explore the foundations of Smart Money Concepts (SMC), including order blocks, fair value gaps, mitigation blocks, and liquidity voids. You’ll also learn about advanced strategies such as the Power of Three (accumulation, manipulation, and distribution), institutional order flow, and high-volatility kill zones like the New York and London sessions. Each section is designed to help you see the market through the lens of professional traders, equipping you with the tools to anticipate price shifts with greater accuracy.
What makes this Smart money trading guide PDF unique is its balance between theory and application. Concepts are explained with real market examples, making them practical for both beginners and experienced traders. By mastering these strategies, you’ll gain confidence in identifying high-probability setups, aligning with institutional flows, and navigating the forex market like a professional.
Excerpts
Institutional trading, also known as smart money trading, provides a glimpse into how price
delivery algorithm is used to manipulate and deliver price in the foreign exchange market.
Smart money is the only trading concept or strategy that has introduced the understanding
the market is not random instead there’s a price delivery algorithm. This thorough guide aims
to explore the world of smart money trading and analyze the strategies that shape the
financial markets.
The Basics of Smart Money Trading
Smart money trading is based on the premise that large financial institutions and major
market participants can manipulate and control prices. This is achieved through the use of
price delivery algorithms, which seek liquidity either on the sell side or the buy side of the
market. Depending on which side of the market price collects liquidity, we can anticipate
either a bearish or bullish order flow.
Are you ready to unveil the power of smart money and gain insights into the strategies
employed by the biggest movers in the financial arena? Let’s embark on this journey into the
heart of the financial world where knowledge becomes power.
1. Order Blocks
Order Blocks are key components of smart money trading. An Order Block represents a
change in the state of price delivery where big participants and banks leave their orders in
the form of sell or buy limits. There are two types of order blocks in forex: bearish order
blocks and bullish order blocks. The bearish order block is the last up candle that forms the
highest high before a downward move, while the bullish order block is the last down candle
that forms the lowest low before an upward move. You can check this article on order block
in forex by ghosttraders
2. Fair Value Gaps
Fair Value Gaps are essential to understanding smart money trading. These gaps occur in
price delivery where one side of the market liquidity is offered, typically confirmed with a
Liquidity Void on lower time frame charts in the same price range. Price can “gap” to create a
vacuum of trading when it leaves a specific level where there’s less trading activity, resulting
in one-directional price movement.
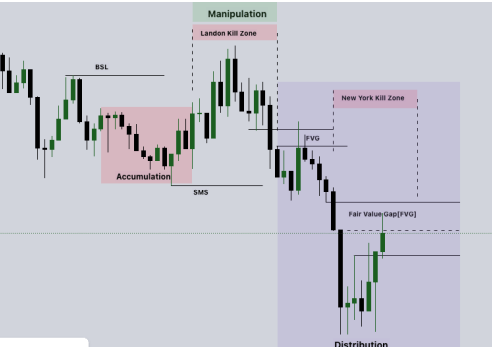
3. Power Of Three
The Power of Three (PO3) is a crucial concept for successful intraday trading. PO3 consists
of three key elements: accumulation, manipulation, and distribution. During accumulation,
price collects orders on both sides of the market. Manipulation occurs when price
deliberately moves in a false direction to deceive traders, while distribution involves the
release of accumulated orders in the market.